Chemical Methods of Control Antimicrobial Drugs
Nucleoside analogs such as acyclovir have proved effective in the chemotherapy of selected viral infections. Get rapid results with our real-time continuous microbial and TOC analyzers.

Exercise25laboratoryreportchemicalmethodsofcontrolantimicrobialdrugs Pdf Sofia Isaksson Bio 203a 07 01 2017 Exercise 25 Laboratory Report Chemical Course Hero
A cidal control measures such as sterilization by heat eg.
. Amphotericin B isolated in the 1950s remains an effective antifungal agent although newer agents such as fluconazole are now widely used. Antimicrobial Agents Modes of Action Cellular targets of physical and chemical agents. Light-induced fluorescence Mie scattering and algorithms.
Later the word antibiosis against life for this inhibition and called the inhibiting substance Antibiotic. Detergent surfactants 9 3. Bacteria typically become resistant to penicillins monobactams carbapenems and cephalosporins are known chemically as beta-lactam antibiotics see Figure 43.
Some antimicrobial drugs detergents and alcohol 2. The sterols are important in maintaining proper membrane fluidity and hence proper function of the cell membrane. The cell wall cell wall becomes fragile and cell lyses.
Keep in mind that chemical treatment is only one of many methods available to control microbial growth. This consitutes an ever more important group of antimicrobials as new drugs with special properties are developed. Autoclaving or by ultraviolet radiation and b static control measures such.
2 and many bacteria become resistant to these antibiotics by producing various beta-lactamases that are able to inactivate some forms of these drugs. An alternative for most β-lactams which require frequent dosing is use of a continuous infusion pump. Top of Page Uses.
Chemical Methods for Cleaning Conventional Dentures. Antifungals take advantage of small differences between fungi and humans in the biochemical pathways that synthesize sterols. Synthetic antimicrobials eg the sulfonamides have always constituted an important source of antimicrobials.
Standardized agar diffusion methods. What is the Best Antimicrobial Option. Figure 149 There are several classes of antibacterial compounds that are typically classified based on their bacterial target.
The cell membrane - loses integrity. Isopropyl alcohol 20 is effective in killing the cysts of Acanthamoeba culbertsoni 560 as are chlorhexidine hydrogen peroxide and thimerosal 496. Antimicrobial drugs involves the use of chemicals to prevent and treat infectious diseases.
Commonly used chemical preservatives include sorbic acid benzoic acid and propionic acid and their more soluble salts potassium sorbate sodium benzoate and calcium propionate all of which are used to control the growth of molds in acidic foods. Each of these preservatives is. The production and use of the antibiotic penicillin in the early 1940s became the basis for the era of modern antimicrobial therapy.
Second the agent must possess chemical stability and should last for about 24 hours after mixing to allow enough time for delivery and administration. Bactericidal antibiotics These antibiotics had killing effects on bacteria. Bacteriostatic antibiotics These antibiotics have an inhibitory effect on bacteria.
NIAID has a substantial research program to spur development of new therapeutics against drug-resistant viruses bacteria parasites and fungi and to identify. The rise of antimicrobial-resistant microbes has led to an urgent need to preserve the efficacy of current antibiotics develop new ones and identify alternative treatment strategies. However such a device can frequently be cost-prohibitive.
Cellular synthetic processes DNA RNA. Chemical preservatives are used to inhibit microbial growth and minimize spoilage in some foods. 4 rows Some synthetic drugs control bacterial infections by functioning as antimetabolites competitive.
The most common mode of action for antifungal drugs is the disruption of the cell membrane. Uses Mueller-Hinton agar which allows antimicrobial agent to diffuse freely. Targets of Antiviral Drugs Antiviral drugs generally target the following.
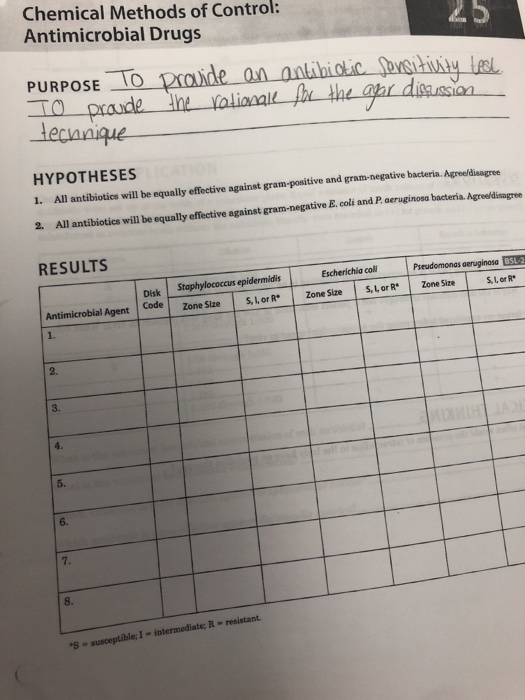
When MIC is determined inhibition zones can be correlated with MICs. Two ways to control microbialinfections. Streptomycin was discovered in 1944 and since then many other antibiotics and other.
Pasteur and others observed that infecting an animal with Pseudomonas aeruginosa protected the animal against Bacillus anthracis. Chemical methods of control. Determined by testing for bacterial growth in dilutions of the antibiotic in nutrient broth 2.
An In Vitro Study Diluted sodium hypochlorite vinegar and chlorhexidine digluconate can be considered adequate products for cleaning dentures due to their potential for inhibiting bacterial growth similar to 1 sodium hypochlorite. The purpose of chemical method of control purpose The purpose is to learn the principle application and evaluation of the Kirby-bauer antibiotic sensitivity test. Why isnt one antimicrobial agent equally effective against all three bacteria.
Biochemical Basis of Antimicrobial Action. Antimicrobial agent any of a large variety of chemical compounds and physical agents that are used to destroy microorganisms or to prevent their development. Structurally characteristics of cell walls and species specific enzyme may vary.
Each class of antibacterial drugs has a unique mode of action the way in which a drug affects microbes at the cellular level and these are summarized in Figure 149 and Table 141. 31 rows Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Minimum inhibitory concentration MIC 1.
Virus-specific enzymes eg reverse transcriptase integrase inserts viral DNA into host DNA proteases process viral proteins Viral DNA replication transcription drugs inhibiting these processes may kill host cell also Fusion of enveloped viruses. What are Antimicrobial Agents. Alcohols are not recommended for sterilizing medical and surgical materials principally because they lack sporicidal action and they cannot penetrate protein-rich materials.
Ad Reliable optical technology. Semisynthetic antimicrobials are those derived from chemical modifications of naturally occurring antibiotics.

Micro Lab Ex 25 Chemical Methods Of Control Antimicrobial Drugs Pdf Course Hero

Lab Ex 02 Chemical Methods Of Control Antimicrobial Drugs Pdf Objectives After Completing This Exercise You Should Be Able To 1 Dene The Following Course Hero
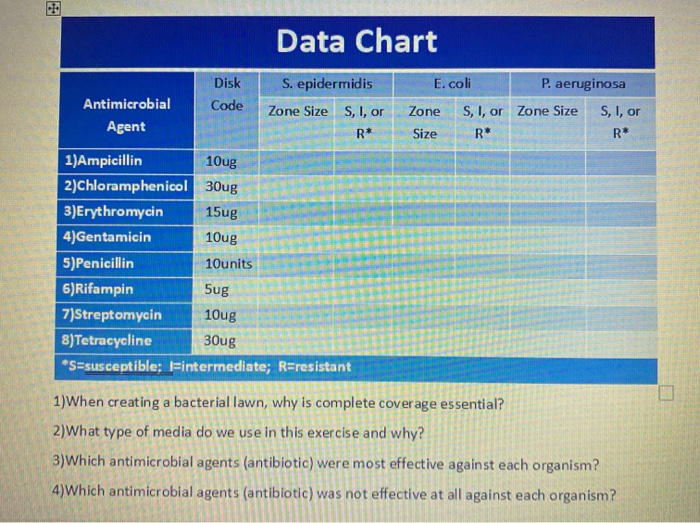
Solved Microbiology Lab Exercise 25 Chemical Methods Of Chegg Com

Solved Chemical Methods Of Control Antimicrobial Drugs Chegg Com
No comments for "Chemical Methods of Control Antimicrobial Drugs"
Post a Comment